What Subcontractors Need to Understand About the Three Levels of CMMC 2.0
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) program continues to evolve, bringing significant changes and implications for businesses operating within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB). As the rulemaking process progresses and updates are introduced, it becomes crucial for subcontractors in the DIB to stay informed about these changes and understand the key points that can impact their operations. Let’s walk through the essentials of CMMC to better understand its evolution and the key aspects subcontractors in the DIB should be aware of.
CMMC 2.0 Explained
CMMC is a framework established by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) to assess and enhance the cybersecurity posture of organizations within the DIB. It aims to protect sensitive information and ensure that adequate cybersecurity practices are in place throughout the contractor supply chain.
As the CMMC program evolves, it is essential to stay up-to-date. Currently, we’re still waiting for the rulemaking process to complete as the requirements and implementation guidelines for CMMC are finalized. The DoD releases updates and news as they have new developments, but it has proven to be a challenge for businesses to navigate, especially when it comes to which requirements they need to meet. Here is what we know so far about this process.
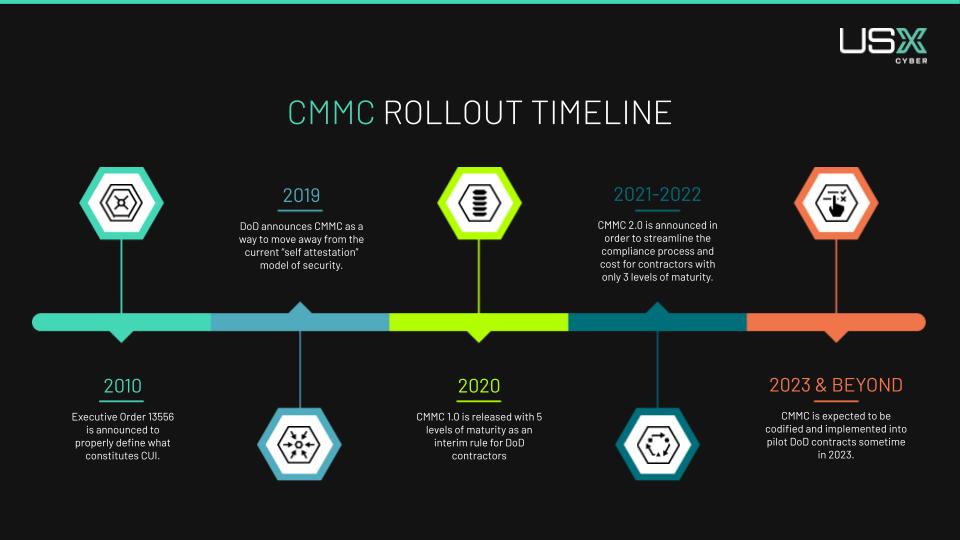
The CMMC framework originally consisted of five levels, each representing an increasing level of cybersecurity maturity. This has since been reduced to 3, with Level 3 controls yet to be finalized. Contractors will be required to meet specific requirements outlined in one of these levels based on their involvement in handling sensitive DoD information.
To oversee the certification process, training, and assessment of contractors, the CMMC Accreditation Body (CMMC-AB) was established. They work with Certified Third-Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAOs). C3PAOs play a crucial role in assessing and certifying organizations’ compliance with CMMC.
That being said, we still don’t have a concrete date for when this framework will be codified and start appearing in new DoD contracts. In the meantime, we are seeing prime contractors starting to proactively enforce compliance among their subcontractors. This is to ensure a seamless transition once CMMC is released, and that all partners are doing their due diligence when it comes to protecting our most important information.
CMMC Levels and Subcontractors
It may feel daunting to subcontractors understanding each level of CMMC and the required controls, on top of assessment and ongoing support. While the framework is still waiting to be codified, we do know that each contractor will only need the level of compliance aligned with the data that they specifically work with, not what’s defined in the contract as a whole. For example, if a prime contractor is compliant at Level 3, but they only pass FCI data to their subcontractors, that subcontractor only needs to be certified at a Level 1.
So, what do all the levels entail? And which one is right for your business? We’ve outlined them below to help you get started.
Level 1
At Level 1 certification within the CMMC framework, organizations in the defense industrial base are expected to have basic cybersecurity practices in place. It consists roughly of 17 controls and is for organizations that only process federal contract information. This is intended for contractors only working with Federal Contract Information (FCI). At this level, you can self-assess.
Level 2
Level 2 certification is meant for organizations processing controlled unclassified information (CUI) data. At this level, organizations will be expected to meet at least 110 controls derived from NIST SP 800-171. Organizations at this level will also require an assessment from an approved and authorized third-party provider.
Level 3
While Level 3 controls have yet to be finalized, the government is actively working to define these at the time of publishing this article. This level is intended for organizations who process CUI data but at a higher, more sensitive nature. As of now, we know that at a minimum Level 3 contractors will need to follow 110+ security practices based on NIST SP 800-171 and -172. Assessments at this level will also go through a government-led assessment, rather than a self-assessment or working with a third-party.
What’s Next for CMMC?
As the CMMC program continues to evolve, businesses within the DIB must stay well-informed about the framework and its evolving updates. By staying engaged and keeping track of the direction of this framework, subcontractors can signal trust to their clients and partners, continually enhance their cybersecurity posture, and ensure compliance readiness.
Our best advice is to stay proactive. If you are overwhelmed or unsure of how this process may affect your business, you can engage with a trusted cybersecurity partner like USX Cyber, and leverage our expertise to support your CMMC journey. To start, check out our webinar on CMMC for more information or reach out to our experts directly so we can help protect sensitive information, strengthen the defense supply chain, and contribute to a more secure future.
Remember, CMMC compliance is not a one-time task but an ongoing commitment to maintaining robust cybersecurity practices within the Defense Industrial Base.
5 Steps for Improving Remote Work Security: Best Practices to Follow Today
If you’re a business owner, you know that the remote work trend isn’t slowing down. And while there are many benefits to allowing employees to work remotely, there are also real cybersecurity risks that come with it. This makes the need for robust remote work security practices more important than ever before.
In this quick guide, we’ll share some of the best practices for remote work security and steps to follow today to help keep your data and systems secure. Whether your business is just transitioning to a remote work environment or you’ve been remote for a while, smart security procedures can protect your business.
What is remote security?
Remote work security refers to the protocols and measures that a company puts in place to protect its employees who work remotely, i.e., outside of the standard office setting. This can include everything from ensuring that data is properly encrypted and stored on secure servers to providing employees with access to virtual private networks (VPNs) so they can connect to the company network securely.
Today’s dispersed workforces make remote security a crucial component of your small business operations. And while the need is fairly obvious, putting it into practice takes some planning and work. But don’t worry; at USX Cyber, we’ve got you covered with the steps you need to get started.
5 Steps to Improving Remote Work Security
There’s no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to remote cybersecurity. However, we’ve compiled 5 steps for you to follow today in order to improve your remote work security and begin building a set of best practices.
- Establish a remote security policy.
- Restrict access to sensitive data to authorized users only.
- Use encryption to protect data.
- Use a VPN to connect to the company network remotely.
- Train employees on how to work securely.
1. Establish a remote security policy.
Perhaps the single most important step you can take is establishing a remote security policy. This should include a set of IT security guidelines that govern how employees who work remotely should access and use company resources. The purpose of a remote security policy is to protect an organization’s data and systems from being compromised by unauthorized users, as well as ensure that all remote workers have the necessary tools and training to work securely.
There are many factors you need to consider when creating a remote security policy for your business. The most important factor is the type of data that will be accessed remotely. Other factors include the level of access needed by users, the sensitivity of the data, and the potential for data loss.
2. Restrict access to sensitive data to authorized users only.
Another critical measure you can take to protect your business from data breaches and other security risks is to restrict access to sensitive company data to authorized users only. This means that only employees who need access to the data to do their jobs should be given access and that access should be limited to what is necessary for them to do their work.
Restricting access is important not just because it helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data. It also helps ensure that employees are using company resources safely and securely.
3. Use encryption to protect data.
Encryption is key to protecting your small business in a remote work environment. Simply put, encryption is the process of transforming readable data into an unreadable format so that it cannot be accessed by unauthorized users. Encryption should be used both while data is in transit, i.e. being sent over the internet, and when it is stored on servers or devices.
Encrypting data helps protect it from being accessed by unauthorized users, whether they are outside the company or inside the network. It also helps ensure compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and PCI-DSS. So if you handle credit card transactions or operate in the healthcare industry, encryption is all but required to do business.
4. Use a VPN to connect to the company network remotely.
A VPN, also known as a virtual private network, helps to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. This extra layer of protection provides a secure connection to the company network, which helps safeguard your data and systems from being compromised. It also allows you to access company resources, such as files and applications, from any location — which is especially relevant with a remote workforce.
There are several different VPN providers available, so it’s important to choose one that meets your needs. The most important factors to consider when choosing a VPN provider are the level of security they offer, the features they provide, and the price.
Once you’ve chosen a VPN provider, the next step is to set up the connection. This process varies depending on the provider you choose but typically involves creating an account and downloading and installing the software. Once installed, you simply open the software and enter your login information to connect to the VPN.
5. Train employees on how to securely work remotely.
Employees are your greatest resource, but they can often be the weakest link in an organization’s cybersecurity defenses. That’s because they may not be aware of the risks posed by cyber threats, or they may not know how to protect themselves and the company from these threats. It’s your job as a business owner to ensure your employees are well-trained on how to securely work remotely.
Training employees on cybersecurity matters is essential for protecting your business from data breaches and other security risks. Employees need to be aware of the dangers posed by cyber threats and know how to protect themselves and the company from these threats. They should also be familiar with the company’s remote security policy and understand how to comply with it. But just as important is drafting your policy so that it is clear and comprehensible for employees of all technical abilities.
The best way to train your employees on cybersecurity is through a combination of online training courses and hands-on training. Online courses can provide employees with a basic understanding of cybersecurity concepts, while hands-on training allows them to apply what they have learned in a safe environment.
Protect Your Remote Business Today
Working remotely can be a great way to attract top talent and give your employees flexibility. However, it is by no means without risk. Running a remote small business requires a specialized cybersecurity plan.
And that’s exactly what USX Cyber specializes in. Whether you do business in-person, in the cloud, or entirely remotely, — our exclusive GuardientTM Extended Detection and Response (XDR) platform stands ready to protect your organization.
Contact one of our expert analysts today to find out how easy it is to get the cyber protection you need.
How Government Subcontractors Can Use Compliance to be More Competitive
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a game-changer in the defense industry, and its implementation is on the horizon. While the immediate impact may not be felt on existing contracts, the lack of CMMC compliance could hinder subcontractors from bidding on crucial business opportunities. Let’s explore the value CMMC brings to subcontractors and what these small businesses should do to capitalize.
CMMC Makes Subcontractors a More Attractive Partner
While the government has yet to finalize the CMMC framework, we’re seeing more prime contractors work to proactively achieve compliance and ensure their subcontractor supply chain partners do the same. Many businesses want to avoid problems staffing or completing the work in contracts due to compliance holding up the process.
As a subcontractor, CMMC doesn’t just communicate compliance. It also communicates how seriously you take cyber hygiene in general. This is a demonstration of trust and reliability for potential business partners and new contracts, even if it’s not required. A proactive approach to CMMC compliance today could serve as a strong external validation of your cybersecurity practices overall. Your demonstrated commitment to cybersecurity along with proactive business procedure can really stand out among other bidders.
How Long Does it Take to Get Certified?
There is no set timeline for compliance. In the marketplace, we’re seeing around 6-12 months of work to get to the assessment portion of compliance, but this relies heavily on the business and the pace they want to set.
Because so many of these controls will affect daily and core operations, this timeline can be expedited or delayed based on how quickly these processes can be – or you’d like them to be – incorporated. At USX Cyber, we can get a client to compliance in as quickly as 90 days, but some businesses prefer more time to understand and incorporate the necessary procedures and documentation into their business operations.
This is yet another reason why it’s important for subcontractors not to separate compliance from protection. When you develop a cybersecurity plan with compliance in mind, rather than fixating on a singular piece of the puzzle, your business is holistically starting with a leg up against the competition.
Improving Cybersecurity Posture With CMMC in Mind
When small businesses look for comprehensive cybersecurity solutions that include CMMC, the benefits aren’t just external, they will see advantages in their operations and their bottom line. Rather than pay for cybersecurity and CMMC as separate products, at USX Cyber we advise our clients to develop a singular roadmap that protects their business overall while supporting their need for CMMC compliance. This ensures ongoing protection that takes into account the systems, assets and teams that are part of the dynamic defense your company needs.
Cybersecurity does not have to break the bank for small businesses. Contact us today for a free CMMC consultation and roadmap with our experts.
5 Types of Phishing Scams Employees Need to Watch For
No one is immune to a phishing attack. In fact, even the most tech-savvy individual can fall victim to a clever scam.
Protection starts with education. And as an employee, it’s important for you to be able to identify the different types of phishing scams used by hackers so you can protect yourself and your company from becoming the next victim. Below are five of the most common types of phishing scams to watch out for. But first, let’s take a look at what defines a phishing attack.
What is a phishing scam?
Phishing is a cybercrime in which the perpetrator contacts the target, posing as a legitimate institution, in order to lure them into providing sensitive data. This data can include login credentials, financial information, or other personal data that can be used for identity theft or other malicious purposes.
One of the biggest problems is that phishing attacks can be notoriously difficult to detect, as the perpetrators often use spoofed email addresses and websites that look identical to the real thing.
5 Types of Phishing Scams
While this type of cyber attack has been around for years, phishing scams continue to evolve, making it difficult to keep up with the latest shifts. However, you can reduce your cyber risk by knowing the five common ways that scammers try to trick their targets:
- Spear Phishing
- Executive Phishing
- Smishing
- Vishing
- Angler Phishing
Spear Phishing
This type of email scam is typically initiated by an external threat attempting to leverage personal information for financial gain or identity theft. Spear phishing emails are often hard to spot because they can look like legitimate emails from companies or organizations that you are familiar with. These types of scams usually target individuals who work in finance or accounting, as well as those who work with sensitive information.
To avoid falling victim to a spear phishing scam, be suspicious of any email that asks you for personal or financial information, even if it looks like it’s from a trusted source. If you’re not sure whether an email is real or not, stop immediately and contact the company or organization directly to confirm its authenticity.
Executive Phishing
The second common type of phishing scam is similar to spear phishing, but it targets high-level executives within an organization. The attacker will often impersonate someone in a position of authority, such as the CEO or CFO, in order to get sensitive information from the employees they manage.
Executive phishing emails can be extremely difficult to spot, as they often mimic the writing style of the executives they’re impersonating. These types of scams usually target organizations rather than individuals, and they can have a devastating impact on the company if sensitive information is leaked.
Steering clear of an executive phishing scam means you need to be suspicious of any email that asks you to do something outside of your normal job duties, even if it’s from someone in a position of authority. If you’re not sure whether an email is real or not, contact the person directly to confirm. It’s better to be safe than sorry, especially in this case.
Smishing
While the word might sound made up, smishing is all too real. This type of scam uses text messages instead of emails to try and trick the recipient into giving away sensitive information. Hackers will often pose as a trusted organization, such as a bank or credit card company, and try to get the target to provide login credentials or financial information.
Smishing attacks can be tricky to detect, as text messages from these compromised sources can appear to be legitimate. These types of scams usually target individuals who are less likely to be aware of phishing scams, such as the elderly or those who are not familiar with the technology.
To avoid falling victim to a smishing attack, be suspicious of any text message that asks you for personal or financial information, even if it looks like it’s from a sender you recognize. If you’re not absolutely sure whether the text message is real or not, contact the company or organization directly to confirm.
Vishing
While the name is different, the game is always the same. Vishing uses phone calls instead of emails or text messages to try and trick the recipient into giving away sensitive information. The hacker will often pose as a credible contact, such as a bank or credit card company, and try to get you to provide user names, passwords, or even account information.
Vishing attacks can be tough to spot since phone calls can sound like they’re from someone you know. These types of scams usually go after the same individuals that smishing scams target.
Being a skeptic can help keep you safe from a vishing attack. That means you should be highly suspicious of any phone call that asks you for any sort of confidential information. If you’re not sure whether a phone call is real or not, hang up. It’s not rude; it’s having cyber smarts. You should then call back and ask for confirmation.
Angler Phishing
Angler phishing is catching more and more people due to its novelty. This new type of phishing attack goes after people via social media. In this scam, the attacker pretends to be a customer service representative and uses social engineering techniques to try to trick the user into giving them personal information or access to their account. This type of attack is becoming more common as social media plays an increasingly integral part in our lives.
The best way to thwart an angler phishing attack is to be wary of any unsolicited messages from customer service representatives. Do not click on any links or attachments that they send, and under no circumstance should you give them any personal information. If you are unsure whether a message is on the up-and-up, reach out to the company through their official website or customer service number.
Stay Up to Date on Cybersecurity Risks
Unfortunately, phishing remains one of the most common and dangerous cyber threats that businesses face because hackers know it works. But being vigilant and aware is something we all must do to limit the potential damage. So that means it’s important for you to be able to identify the different types of phishing attacks in order to protect yourself and your company from falling victim.
At USX Cyber, we fulfill our mission of protecting small businesses by keeping you up-to-date on the latest cybersecurity trends. That’s because when you are better informed, you can stay better protected. And as hackers try to find new ways in, you can rest assured that our highly trained cyber analysts have already found a way to stop them. Contact us today to get advanced protection for your business before you need it.
USX Cyber Earns Three Gold Cybersecurity Excellence Awards
We are excited to announce that USX Cyber has been honored with three Gold 2023 Cybersecurity Excellence Awards within the following categories:
- Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP)
- Cybersecurity Posture
- Managed Detection and Response (MDR)
The Cybersecurity Excellence Awards recognize companies, products, and professionals that demonstrate excellence, innovation, and leadership in information security. Winners are selected based on qualities such as demonstrated leadership, excellence and results in cybersecurity and the popular votes and comments received from the cybersecurity community.
“We are honored to receive these awards, which reflect our team’s dedication to providing innovative and effective cybersecurity solutions to our clients,” said Clyde Goldbach, Jr., CEO of USX Cyber. “As cyber threats continue to evolve, our team remains focused on staying ahead of the curve and providing our clients with the best possible protection against these threats, no matter the size. We are proud to be recognized for our efforts and look forward to continuing to defend businesses that didn’t have access to this protection before.”